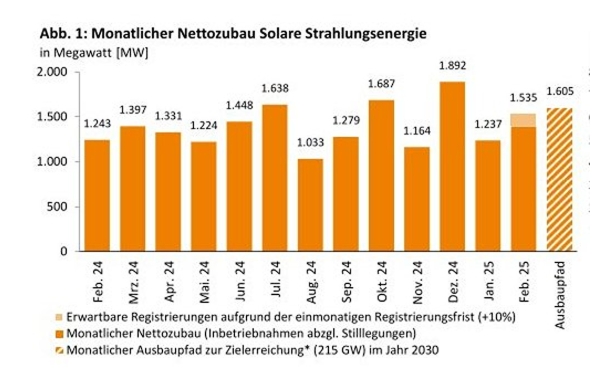
The country’s installed nuclear capacity grew 9% in 2019.

China should increase its nuclear capacity by more than 40% between 2020 and 2025, with six to eight nuclear reactors commissioned per year. The country should raise total nuclear power capacity from 48.7GW in end-2019 to 70GW in 2025. In the short run, however, China is expected to miss its 2020 target of 58GW as the country’s nuclear capacity should stand at 52GW by the end of 2020.
After an 18% growth in 2018, the country’s installed nuclear capacity grew 9% in 2019, from around 44.6GW to 48.7GW, with the connection of two reactors to the grid (Yangjiang-6 and Taishan-2). In addition, 12 nuclear reactors totalling 12,244MW are currently under construction and another 42 reactors are planned with a combined capacity of 48,660MW.
According to the National Energy Administration, China's nuclear power generation rose by more than 18% in 2019, raising the share of nuclear in the power mix from 4.1% to 4.9%. Overall, power generation in China grew by 5.2% and thermal power plants still accounted for 72% of the power mix, followed by hydropower (16%), wind (5%) and solar (1.6%).