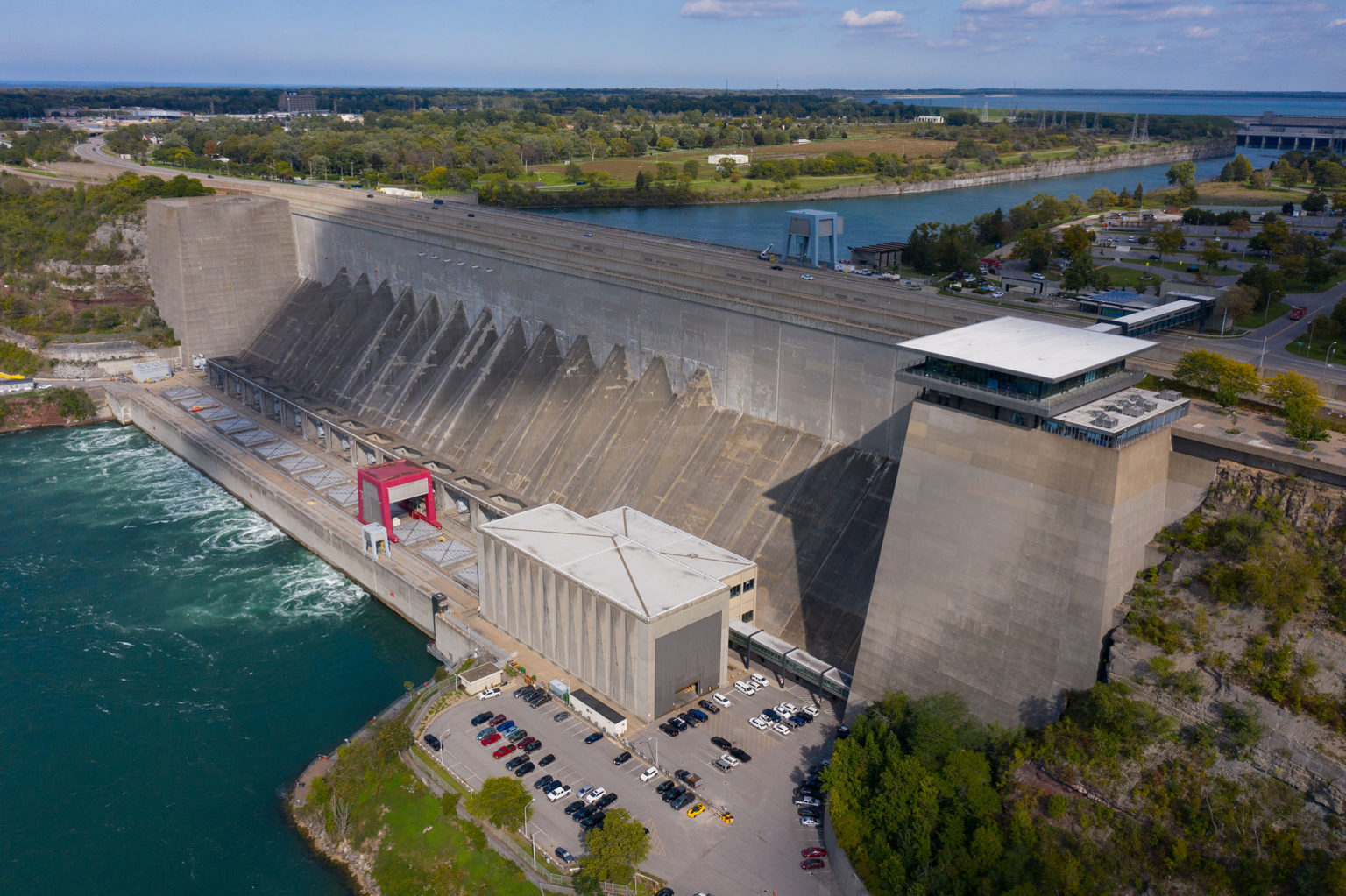
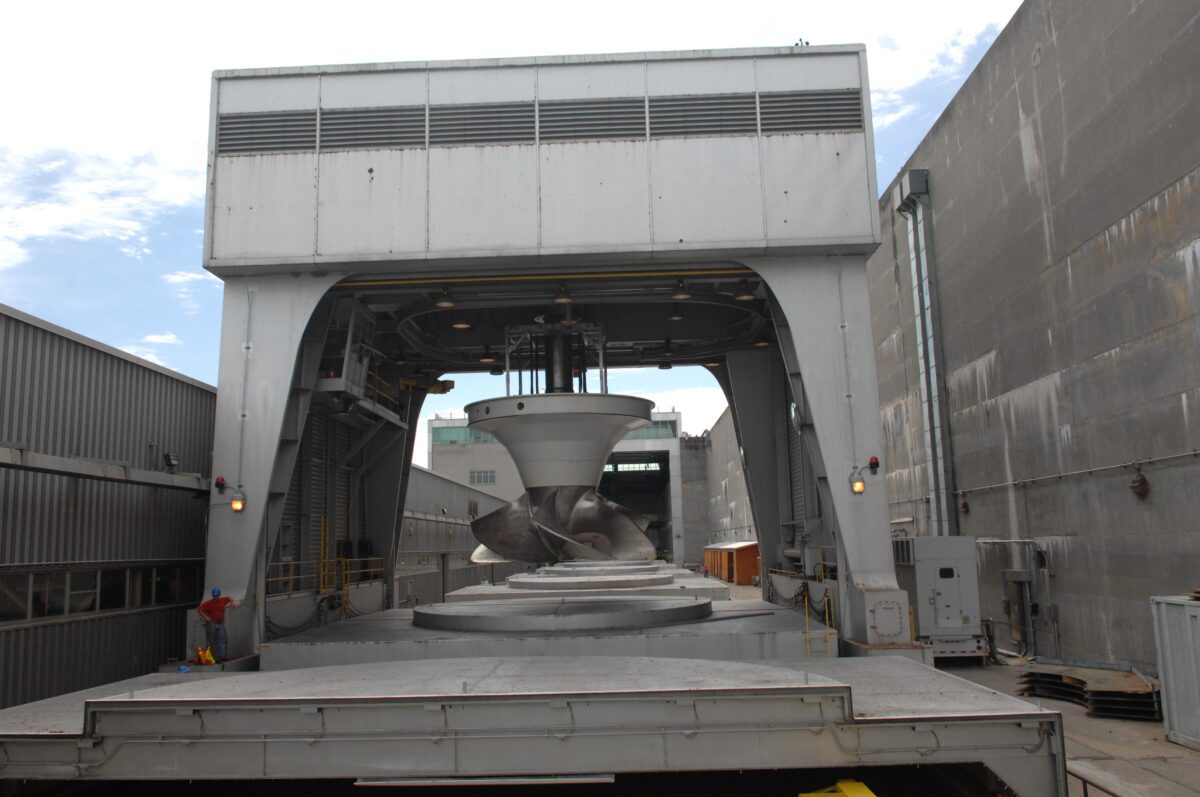
Robert Moses Niagara Power Plant (photo courtesy NYPA)
The New York Power Authority reports it has completed work on the first major upgrade of the Niagara Power Project’s control room since the plant was built in 1961.
The control room upgrades and digitalization, conducted over a nine-month period in 2022, are a signature part of NYPA’s 15-year modernization and digitization program, dubbed Next Generation Niagara (NGN), that will extend the operating life of the Niagara Power Project.
The 2,675 MW Niagara Power Project in western New York is the state’s largest producer of electricity. This $1.1 billion commitment will focus primarily on the Robert Moses Niagara Power Plant, the larger of two plants that comprise the Niagara Power Project. The plant – located in Lewiston — contains 13 turbine-generator units with a total capacity of 2,525 MW.
This control room contains the remote operating controls for the entire Niagara Power Project, including the Robert Moses Power Plant, the Lewiston Pump Generating Plant and associated switchyards. The control room upgrades are designed to improve operator performance and bolster cybersecurity. New features include a large video display board, better lighting, noise canceling architecture and sit/stand desks. The upgrades are vital to ensure the facility will continue to help New York State meet its clean energy goals as outlined in the Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act, according to a release.
“The upgrade and digitization of our Niagara Power Project’s controls is a foundational pillar in our multi-year modernization effort to ensure that New York’s flagship clean energy power plant is leading the way in hydropower generation for the state for the next 50 years,” said NYPA Acting President and Chief Executive Officer Justin E. Driscoll. “The complete control room overhaul is the centerpiece of our Next Generation Niagara life extension and modernization program. We are digitizing the entire plant, turbine by turbine. We also are taking this opportunity to make workplace design improvements for the health and safety of our operators that conform to best industry practices.”
Launched in July 2019, the NGN initiative encompasses four phases:
Design and implementation of an inspection platform to conduct comprehensive inspections of the Robert Moses Plant’s penstocks;
Replacement of the 630-ton gantry crane that enables disassembly and reassembly of the generating units;
Upgrading and digitizing control systems (the engineering, procurement and construction contract for this work was awarded to Burns & McDonnell in December 2019); and
Overhaul and/or replacement of mechanical components that have reached the end of their operating life.
New York State’s climate agenda calls for an orderly and just transition that creates family-sustaining jobs, continues fostering a green economy across all sectors and ensures that at least 35%, with a goal of 40%, of the benefits of clean energy investments are directed to disadvantaged communities. New York is on a path to achieving a zero-emission electricity sector by 2040, including 70% renewable energy generation by 2030, and economywide carbon neutrality by mid-century. A cornerstone of this transition is New York’s clean energy investments, including more than $35 billion in 120 large-scale renewable and transmission projects, $6.8 billion to reduce building emissions, $1.8 billion to scale up solar, more than $1 billion for clean transportation initiatives, and over $1.8 billion in NY Green Bank commitments.
NYPA is the largest state public power organization in the U.S., operating 16 generating facilities and more than 1,400 circuit-miles of transmission lines. More than 80% of the electricity NYPA produces is clean renewable hydropower.