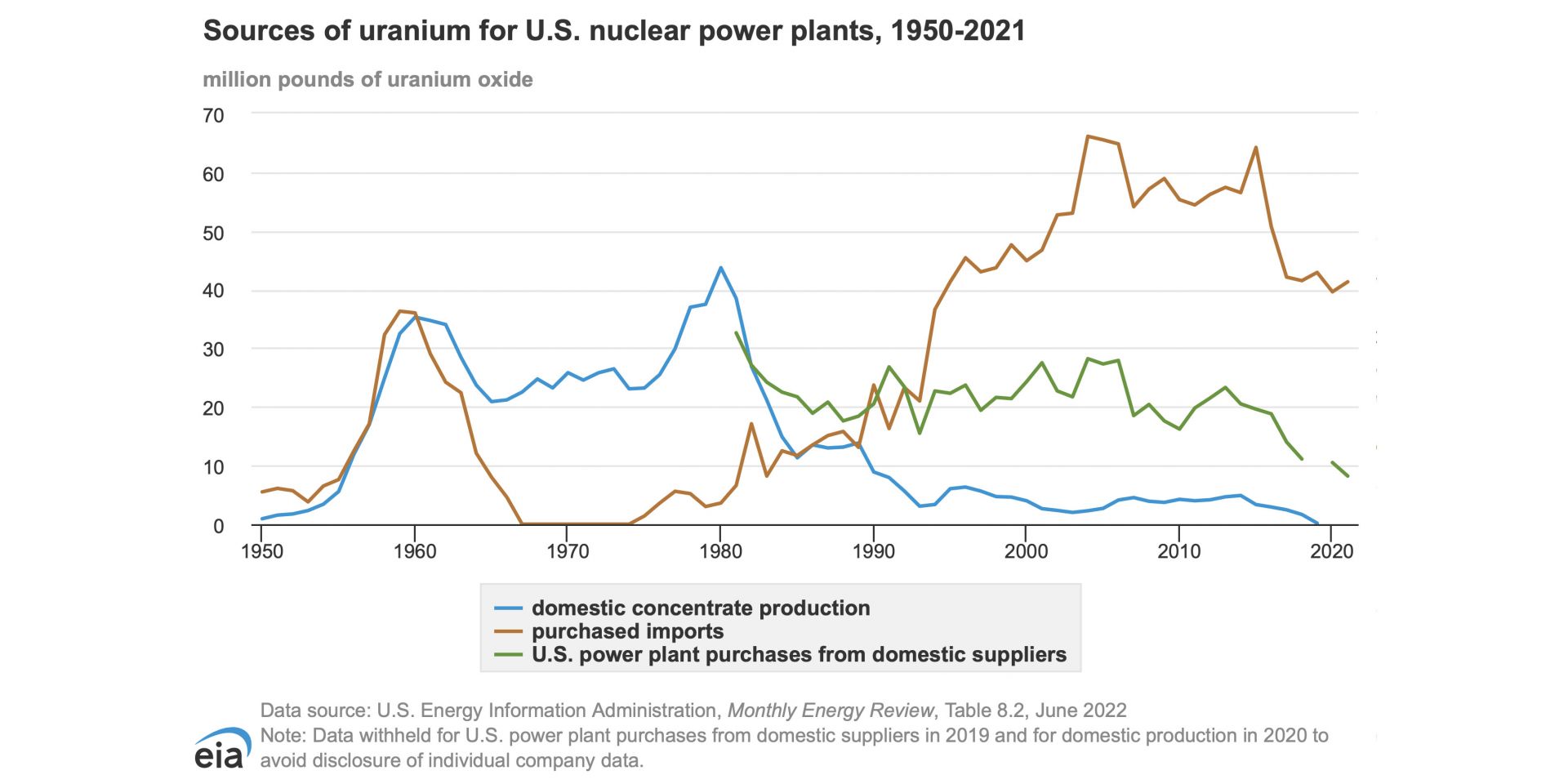
This chart from the EIA shows sources of uranium for U.S. nuclear power plants, 1950-2021. In 2020, according to the chart, 39.60 million pounds of uranium oxide was imported for the domestic nuclear power plant fleet. (Credit: Energy Information Agency)
The naturalist John Muir is widely quoted as saying, “When we try to pick out anything by itself, we find it hitched to everything else in the Universe.” While he was speaking of ecology, he might as well have been talking about nuclear fuel.
At the moment, by most accounts, nuclear fuel is in crisis for a lot of reasons that weave together like a Gordian knot. Today, despite decades of assertions from nuclear energy supporters that the supply of uranium is secure and will last much longer than fossil fuels, the West is in a blind alley. We find ourselves in conflict with Russia with ominous implications for uranium, for which Russia holds about a 14 percent share of the global market, and for two processes that prepare uranium for fabrication into reactor fuel: conversion (for which Russia has a 27 percent share) and enrichment (a 39 percent share).