Unsurprisingly, solar panels are becoming increasingly popular to help protect the planet and secure future clean and renewable energy. However, a significant challenge remains: what happens to the excess electricity solar panels produce when it is not utilised? This extra energy is often wasted, resulting in missed opportunities and inefficiencies in using renewable energy. To maximise the efficiency and sustainability of solar panel installations, more innovative solar technology ensures that no clean energy goes to waste. It effectively stores and manages excess energy by repurposing surplus energy through a system that minimises the environmental impact of solar panels, further promoting the adoption of renewable energy and reducing reliance on traditional power sources.
Solar energy and the potential for unused electricity
The reliance on non-renewable energy sources has become increasingly clear that finding alternative solutions is key. Solar energy has emerged as a promising option, as it's both renewable and abundant in most parts of the world. One of the biggest benefits of solar energy is the excess electricity it generates, which often goes unused. Photovoltaics (PV) have revolutionised the way to generate and consume electricity. Photovoltaic systems are a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels since they use the sun's energy. The sun's energy to the earth for one hour could meet the global energy needs for one year. However, not all this energy can be collected, and solar panels often generate unused electricity. One way to address this issue is to store excess electricity in solar batteries for later use. This can be particularly useful for off-grid applications or when there is little sunlight. Another option is to feed excess electricity into the electrical grid, which can earn money through the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG).
In addition, advancements in solar panel technology have improved efficiency and lower production costs, making solar energy more accessible and cost-effective for consumers. The conversion efficiency of panels has been enhanced by 0.5% each year for the last ten years, even as production costs have sharply declined.
Governments and private organisations invest in solar farms and infrastructure to better capture and distribute solar energy. Incentives are also available for homeowners and businesses to install solar panels, which can help reduce energy bills and promote a cleaner environment. The potential for unused solar energy is enormous and can help reduce the reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
Solar panels can generate excess electricity during summer. The extra electricity is sent back to the grid, and the homeowner receives credits from the utility company based on the net kilowatt-hours given to the grid. During winter, the homeowner can draw power from the credits accumulated throughout the summer. If the solar panels generate more electricity than is required, the homeowner can sell the surplus to the grid.

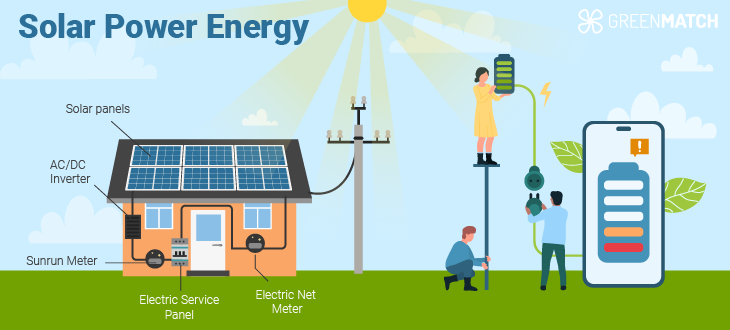
What happens to unused electricity generated by solar panels?
Have you ever wondered what happens to the excess electricity solar panels generate? Well, the answer is quite simple. Any excess electricity on the solar panels can be sent back into the grid. This is known as net metering.
There are several options for what to do with the excess energy:
1. Store it in batteries: Excess electricity can be stored for later use. This is a great option for off-grid applications or when there is little sunlight.
2. Feed it back into the electrical grid: In most grid-connected PV systems, excess electricity is fed directly into the grid network. This is known as net metering, allowing homeowners to earn credits for the excess electricity they generate. These credits can be used to offset future electricity bills. 3. Home Power: Excess energy can be used later to power the home using solar battery banks. This is a great option when weather conditions are not optimal for solar energy generation.
4. Donate it: Donate the excess electricity to charity. Many organisations accept electricity donations, which would be a great way to help reduce carbon footprint.
The excess electricity generated by solar panels is not wasted potential. It can be used to power other homes and businesses, reducing the reliance on non-renewable energy sources. There are some challenges associated with solar panels. The required solar panel recycling capacity has to be built as part of a comprehensive end-of-life infrastructure also encompassing uninstallation, transportation, and storage facilities for solar waste.
Additionally, there may be a hiatus when people are expected to give away unused energy for free while waiting to implement a new market. This makes energy firms compete to offer solar homes the best price for any unused energy they export.
Storing or selling unused electricity generated
There are several benefits to storing or selling unused electricity generated by solar panels. These options allow homeowners to make the most of their solar energy systems and earn money through net metering or feed-in tariffs. With technological advancements and the potential for unused electricity, solar energy is becoming an increasingly attractive option for consumers and businesses.
Here are some of the benefits of storing or selling unused electricity generated by solar panels:
Storing Unused Electricity
· Cost savings: Storing surplus solar energy in batteries can help reduce electricity bills by allowing homeowners to use stored energy during peak hours when electricity prices are higher.
· Increased energy independence: Storing solar energy in batteries can provide a reliable source of electricity during power outages or when the grid is down.
· Reduced carbon emissions: Storing solar energy can help reduce the need for fossil fuels and decrease carbon emissions.
· Increased efficiency: Storing solar energy can help make the electrical grid more efficient by reducing the need for expensive and inefficient peaker plants.
Selling Unused Electricity
· Earn money: Homeowners can earn money by selling excess electricity to the grid through programs like the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG).
· Reduced carbon emissions: Selling excess solar energy back to the grid can help reduce the need for fossil fuels and decrease carbon emissions.
· Increased grid stability: Selling excess solar energy back to the grid can help stabilise the electrical grid by providing additional sources of electricity during peak demand.
Maximising solar panel renewable energy
In today's world, finding sustainable and renewable energy sources is crucial to meet the growing energy demand at homes and businesses. Solar power is a perfect solution; it is clean, affordable, and abundant.
Here are some tips:
· Ensure ample sunlight and a correct installation: Solar panels need to be installed in a location that receives sunlight throughout the day. Ensuring the panels are installed correctly is important to maximise their effectiveness.
· Keep solar panels clean: Solar panels must be clean and free from dirt, debris, and other materials blocking sunlight. Regular cleaning can help maximise solar energy production.
· Install a solar battery: A solar battery can store excess energy generated by solar panels for use during periods of low sunlight or high energy demand.
· Monitor system performance: Regular monitoring of the solar energy system can help identify any issues affecting its performance. This can help ensure that the system is operating at maximum efficiency.
· Pick a solar partner wisely: Choosing a reputable solar company with a proven track record can help ensure that the solar energy system is installed correctly and operates efficiently.
· Having the right system: Before purchasing a solar energy system, it is important to schedule an energy audit to determine the right plan for the home and energy needs.
Utilising solar power is a practical and long-lasting solution for sustainable energy. Optimising solar panel installations and investing in energy storage is the key to maximising its potential. Additionally, adopting energy-efficient practices and exploring new applications can further maximise the use of solar power. Doing so can build a cleaner and more sustainable future for generations.





