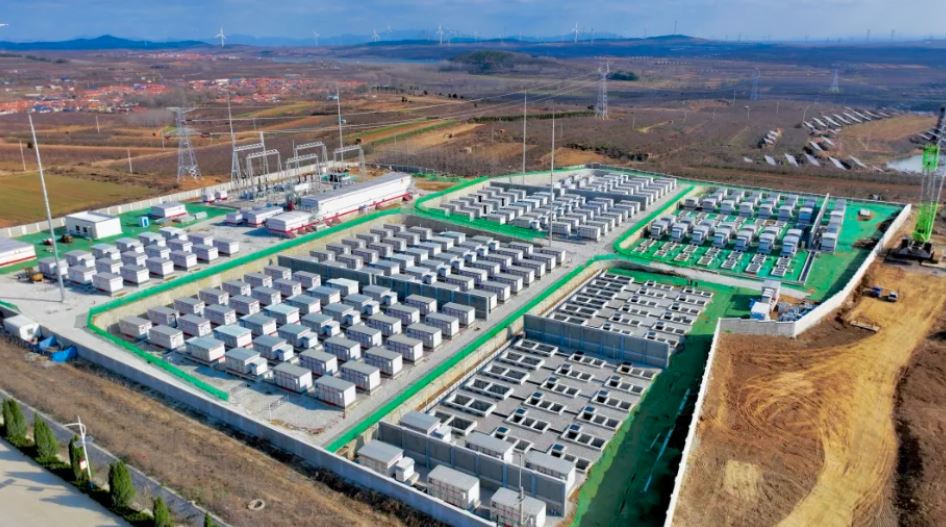
The project consists of 42 BESS containers with 185 Ah sodium-ion batteries, 21 power conversion systems, and a 110 kV booster station. The project is being developed and managed by Datang Hubei Energy and marks China’s efforts to diversify away from lithium to more abundant sources. Datang Hubei Energy said it had started operating the project on July 2. It was connected to the grid on June 30.
As with such ESS systems, the batteries can bridge the highs and lows of renewable energy production to stabilize grids. Chinese media reported that the project in Qianjiang, Hubei province, shows that sodium-ion batteries have become a new possibility for future power grid development. Sineng Electric said that sodium-ion batteries show superior performance at low temperatures, better round-trip efficiency, and better overall safety.
The company said its 2.5 MW string PCS MV solution is designed to align with the sodium-ion battery storage system’s wide DC voltage range, supporting rated output power from 700 V to 1,500 V. The solution features cluster-level energy management that the company says amplifies the cluster-level balancing capabilities of sodium-ion batteries. The company says its string PCS units can endure extreme temperatures and high humidity, engineered with an IP66 protection rating.
Sineng Electric recently commissioned a 100MW/200MWh energy storage project in Shandong province. It also recently signed a supply agreement with German semiconductor chip manufacturer Infineon Technologies AG